Case presentation: Congenitally Missing Tooth Restored
This case was done 5 years ago. Patient was 21 year old female with congenitally missing max right lateral incisor. I performed both surgery and restoration.
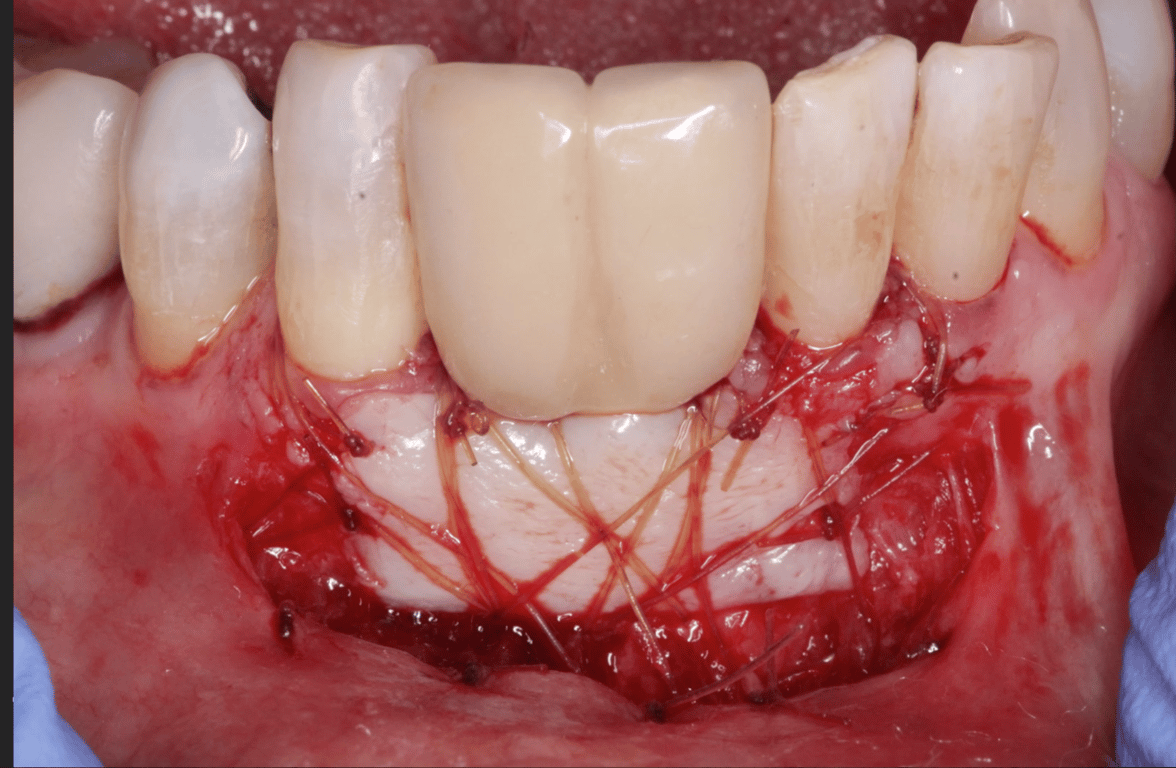
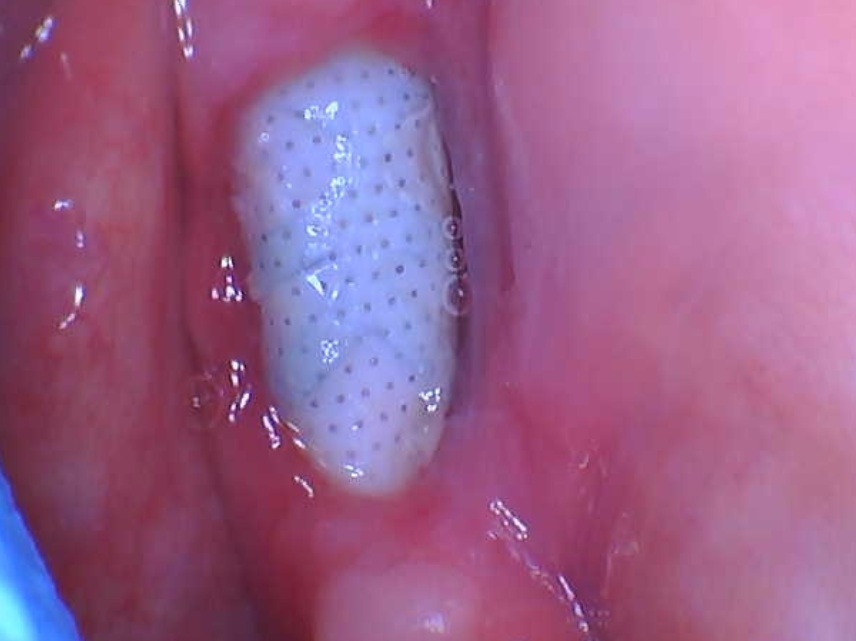
Prior to placing the implant, I took a diagnostic model and waxed up a tooth at #7 position to figure out the exact location of ideal labial margin of final crown and lingual extent of the final crown. Using this information, I fabricated a surgical stent that shows where the final labial margin is. I placed the implant so that there is at least 2 mm of labial bone and the head of implant is located 3 mm apical to the ideal gum line. I under prepped the bone so that the implant has at least 30 NCm of final insertion torque and about 72 ISQ value on Osstell. I fabricated a screw retained implant provisional crown and immediately connected it to the implant and sutured the gingiva around the provisional crown.
I initially under contoured the provisional crown so that I end up with excess soft tissue after healing. After 6 months, I changed the cervical contour of the prov crown to sculpt the gingiva to make it look exactly like that of #10. After I am satisfied with the result, I took an impression fabricated a screw retained porcelain fused metal implant crown. This technique can also be used on extraction cases.
In summary, in order to have a successful outcome these things have to be in place:
1. excellent primary stability
2. min 2 mm of labial bone thickness
3. head of implant located 3 mm apical to the ideal labial gum line
4. platform switched implant
5. proper size implant diameter. bigger is not better when it comes to anterior cases
6. if need to bone graft, use slow resorbing material
7. when contouring prov crown, leave 5 mm of distance from the bone to bottom of proximal contact point (per dr. dennis tarnow’s paper)
8. get rid of any occlusal contacts on prov crown
9. use impression technique that captures the gingival emergence profile (i use open tray technique with flowable composite in the emergence profile and light cure to lock in the shape)
10. use quality lab (the lab tech should be both an artist and technician)
Please feel free to comment on this case.
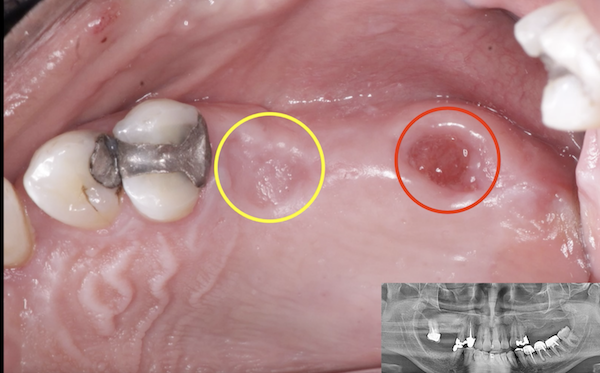
 preop
preop The implant’s Hiossen’s GSII 3.5 mm diameter. the implant’s placed so that the head of implant’s located 3 mm apical from labial margin and there is at least 2 mm of labial bone thickness.
The implant’s Hiossen’s GSII 3.5 mm diameter. the implant’s placed so that the head of implant’s located 3 mm apical from labial margin and there is at least 2 mm of labial bone thickness. this is immediately placed screw retained implant fixed provisional crown 6 months after initial placement. I used the provisional crown to mold the gingival contour to ideal shape.
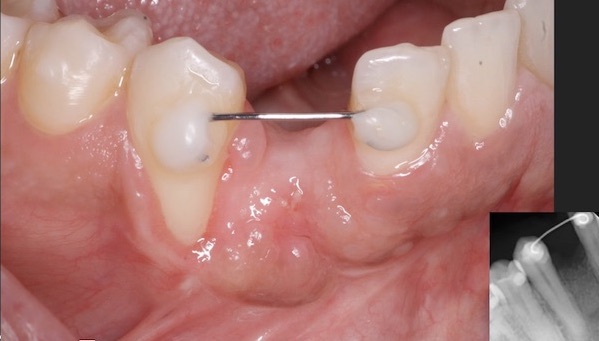
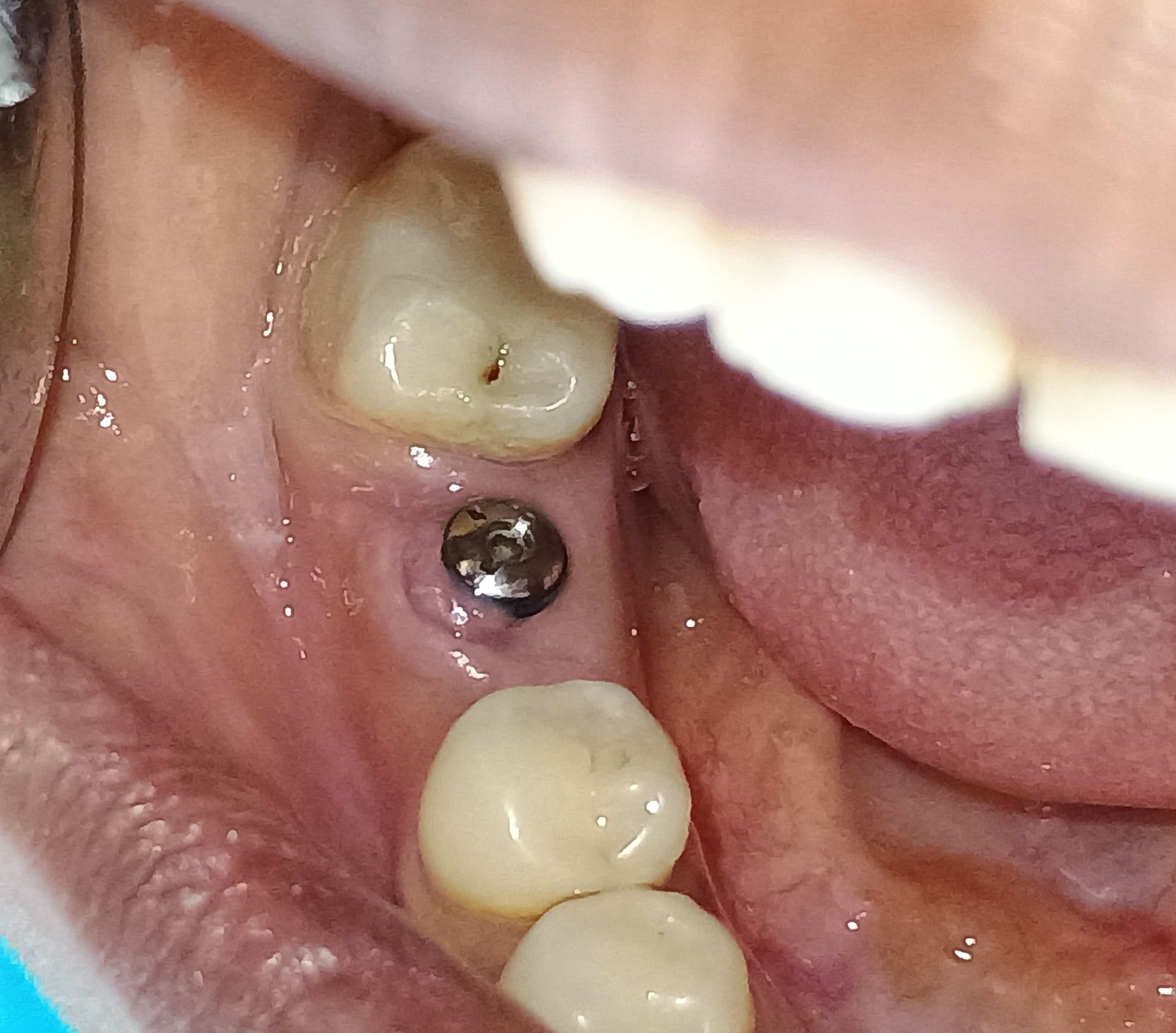
this is immediately placed screw retained implant fixed provisional crown 6 months after initial placement. I used the provisional crown to mold the gingival contour to ideal shape. this picture was taken 5 years after initial delivery of this screw retained implant crown. #10 is a porcelain veneer.
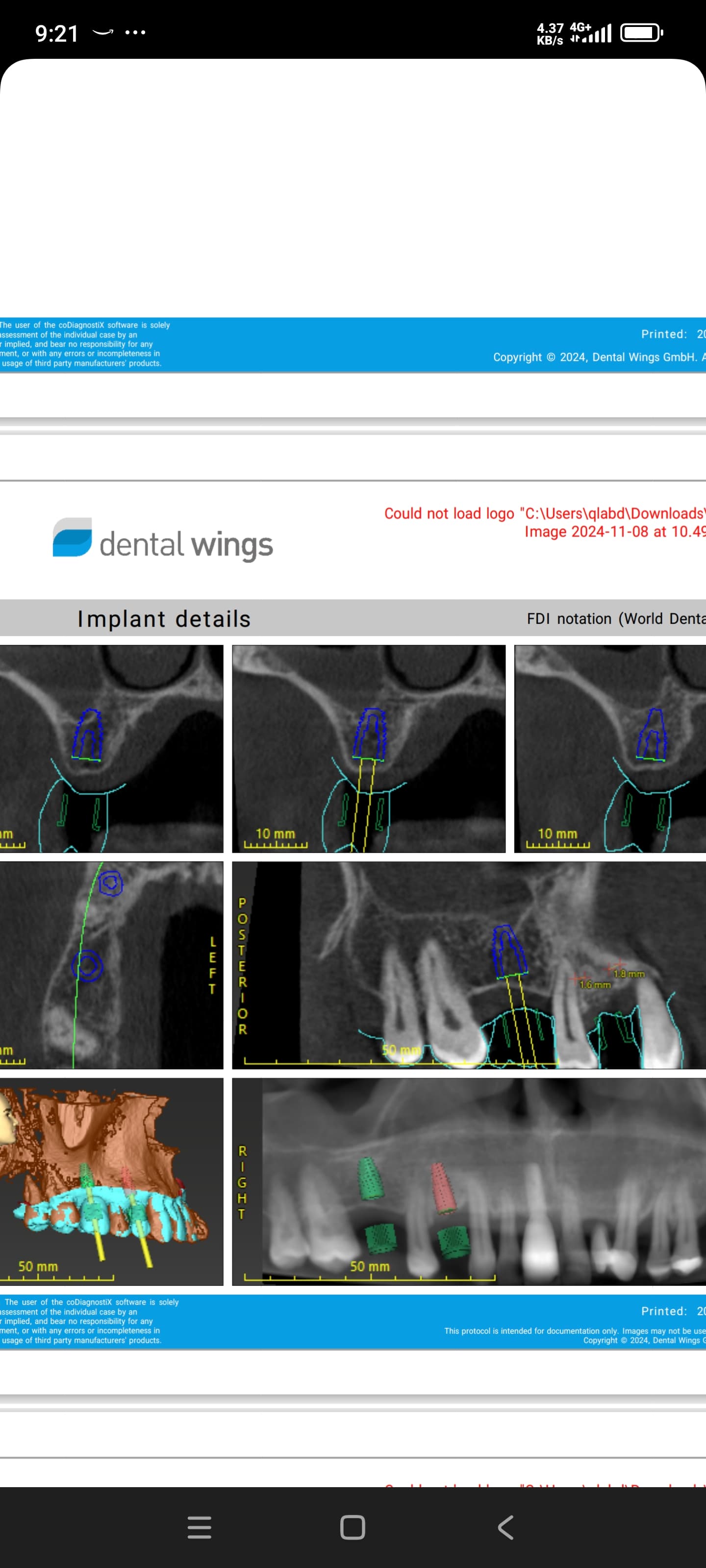
this picture was taken 5 years after initial delivery of this screw retained implant crown. #10 is a porcelain veneer. CT scan was taken at recall appointment. providing at least 2 mm of labial bone at the time of implant placement and placing the implant at correct location coronoapically are some of the key factors in preventing recession.### Some additional case photos for this case:
CT scan was taken at recall appointment. providing at least 2 mm of labial bone at the time of implant placement and placing the implant at correct location coronoapically are some of the key factors in preventing recession.### Some additional case photos for this case:
 These are pictures of diagnostic wax up and vacuum formed stents. One stent is trimmed to ideal labial gum line. The other stent is used to fabricate the screw retained implant provisional crown.
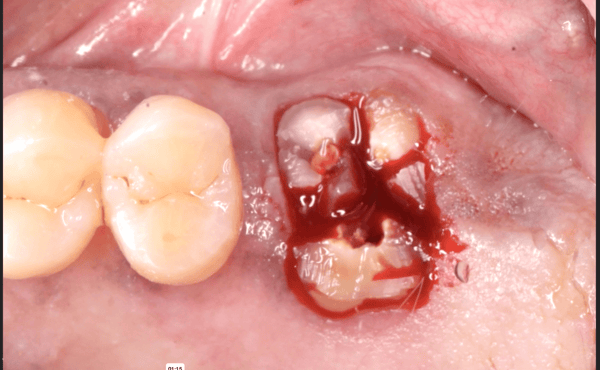
These are pictures of diagnostic wax up and vacuum formed stents. One stent is trimmed to ideal labial gum line. The other stent is used to fabricate the screw retained implant provisional crown. Surgery photos. Note the use of surgical stent to indicate the ideal labial crown margin. In this case, there was excess in bone height, and I had to place the implant subcrestal and remove excess bone. Having this type of surgical stent allows me to place the implant at precise location.
Surgery photos. Note the use of surgical stent to indicate the ideal labial crown margin. In this case, there was excess in bone height, and I had to place the implant subcrestal and remove excess bone. Having this type of surgical stent allows me to place the implant at precise location. These photos shows how I intentionally under-contoured immediate provisional crown so that I will end up with excess soft tissue that I can use later to mold it into the ideal shape by changing the gingival contour of provisional crown.
These photos shows how I intentionally under-contoured immediate provisional crown so that I will end up with excess soft tissue that I can use later to mold it into the ideal shape by changing the gingival contour of provisional crown. #7 is screw retained PFM implant crown and #10 is a porcelain veneer.
#7 is screw retained PFM implant crown and #10 is a porcelain veneer. Photo taken immediately after crown delivery.
Photo taken immediately after crown delivery.